Ashley and Greg performed summer research at Boeing Seattle
Characterization of particle dispersion and volume fraction in alumina-filled epoxy nano composites using photo-stimulated luminescence spectroscopy
Abstract
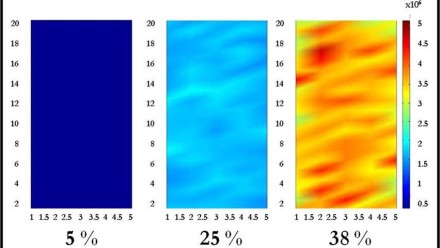
A novel method is presented to validate the dispersion of a-alumina nanoparticles within a polymer matrix, as well as to create a calibration for filler particle volume fraction identification. Using photo-stimulated luminescence spectroscopy (PSLS), spectral information from a-alumina-filled epoxy nanocomposites consisting of varying volume fraction quantities of alumina nanoparticles was collected and analyzed. Surface contour maps of each nanocomposite were created by comparing integrated intensity data from the R1 curve of a-alumina throughout each specimen. These maps show satisfactory dispersion of alumina in the 5 and 25% volume fraction composites, whereas agglomerations were detected in various regions of the 38% nanocomposite, establishing the capability of this method to characterize photo-luminescent particle dispersion. This new approach also provides high spatial resolution, which can be used to determine the exact locations of voids, inclusions and/or agglomerations, while also predicting the volume percentage of photo-luminescent particle content within a specimen, lending itself as a quality control method in the manufacturing of these composites.
Read the full paper at http://www.nature.com/pj/journal/v43/n11/full/pj201182a.html